Bash Pattern Matching
Bash Pattern Matching - Web to match regexes you need to use the =~ operator. Web [[ $string = $pattern ]] doesn't perform regex matching; This works in bash, dash, and just about any other shell you can name. Means any character in regex, it matches only itself in. The word is expanded to produce a pattern just as in. Web regular expressions are a useful tool for pattern matching in bash scripting. Web if you wanted to match letters, digits or spaces you could use: Any character that appears in a pattern, other than the special pattern characters described below, matches itself. Web you can use the test construct, [[ ]], along with the regular expression match operator, =~, to check if a string matches a regex pattern (documentation). Finally, nesting extended patterns is possible, but can be slow if. Patterns are useful not only for filenames and over time found their way into several other shell features. Web learn how to use bash's glob patterns, also known as wildcards, to match filenames and perform pattern matching in your bash scripts. Web to match regexes you need to use the =~ operator. Web case $line in (*$pwd*) # whatever your then block had. Web if you wanted to match letters, digits or spaces you could use: Web you can use the test construct, [[ ]], along with the regular expression match operator, =~, to check if a string matches a regex pattern (documentation). The word is expanded to produce a pattern just as in. Web the * is a special character in bash that represents 0 or more characters. $ {parameter#word} $ {parameter##word} remove matching prefix pattern. Other characters similarly need to be escaped, like #, which would start a comment if not. Web regular expressions are a useful tool for pattern matching in bash scripting. Regex allows users to search, match, and manipulate text patterns with. Web [[ $string = $pattern ]] doesn't perform regex matching; They allow you to define complex patterns and search for matches within. Patterns are useful not only for filenames and over time found their way into. This works in bash, dash, and just about any other shell you can name. Web if you wanted to match letters, digits or spaces you could use: They allow you to define complex patterns and search for matches within. Patterns are useful not only for filenames and over time found their way into several other shell features. Other characters similarly. They allow you to define complex patterns and search for matches within. It can also be used to. Web you can use the test construct, [[ ]], along with the regular expression match operator, =~, to check if a string matches a regex pattern (documentation). Web pattern matching for things other than filenames. A backslash escapes the following character; Finally, nesting extended patterns is possible, but can be slow if. Any character that appears in a pattern, other than the special pattern characters described below, matches itself. The nul character may not occur in a pattern. Web pattern matching for things other than filenames. Web regular expressions are a useful tool for pattern matching in bash scripting. A backslash escapes the following character; Web you can use the test construct, [[ ]], along with the regular expression match operator, =~, to check if a string matches a regex pattern (documentation). Any character that appears in a pattern, other than the special pattern characters described below, matches itself. Other characters similarly need to be escaped, like #, which. Finally, nesting extended patterns is possible, but can be slow if. The nul character may not occur in a pattern. Any character that appears in a pattern, other than the special pattern characters described below, matches itself. Web [[ $string = $pattern ]] doesn't perform regex matching; This works in bash, dash, and just about any other shell you can. Other characters similarly need to be escaped, like #, which would start a comment if not. Web you can use the test construct, [[ ]], along with the regular expression match operator, =~, to check if a string matches a regex pattern (documentation). Web [[ $string = $pattern ]] doesn't perform regex matching; Web if you wanted to match letters,. Web regular expressions are a useful tool for pattern matching in bash scripting. Any character that appears in a pattern, other than the special pattern characters described below, matches itself. Finally, nesting extended patterns is possible, but can be slow if. Patterns are useful not only for filenames and over time found their way into several other shell features. The. So, this command essentially says, cat any files that contain 0 or more characters, followed by.txt. Web apart from grep and regular expressions, there's a good deal of pattern matching that you can do directly in the shell, without having to use an external program. Other characters similarly need to be escaped, like #, which would start a comment if. Web the * is a special character in bash that represents 0 or more characters. This works in bash, dash, and just about any other shell you can name. Regex allows users to search, match, and manipulate text patterns with. The nul character may not occur in a. Web to match regexes you need to use the =~ operator. Web you can use the test construct, [[ ]], along with the regular expression match operator, =~, to check if a string matches a regex pattern (documentation). Web pattern matching for things other than filenames. $ {parameter#word} $ {parameter##word} remove matching prefix pattern. Regex allows users to search, match, and manipulate text patterns with. The word is expanded to produce a pattern just as in. Web case $line in (*$pwd*) # whatever your then block had. Web learn how to use bash's glob patterns, also known as wildcards, to match filenames and perform pattern matching in your bash scripts. Web to match regexes you need to use the =~ operator. Web apart from grep and regular expressions, there's a good deal of pattern matching that you can do directly in the shell, without having to use an external program. They allow you to define complex patterns and search for matches within. Means any character in regex, it matches only itself in. It can also be used to. Other characters similarly need to be escaped, like #, which would start a comment if not. The nul character may not occur in a pattern. Any character that appears in a pattern, other than the special pattern characters described below, matches itself. Web the manpage for bash says:Bash pattern matching Kirelos Blog
Bash pattern matching
Pattern Matching in Bash Delft Stack
Pattern matching on path names in bash (5 Solutions!!) YouTube
Bash pattern matching
Bash Pattern Matching Redefined for Precision
Bash pattern matching Kirelos Blog
Bash pattern matching Kirelos Blog
Bash pattern matching Kirelos Blog
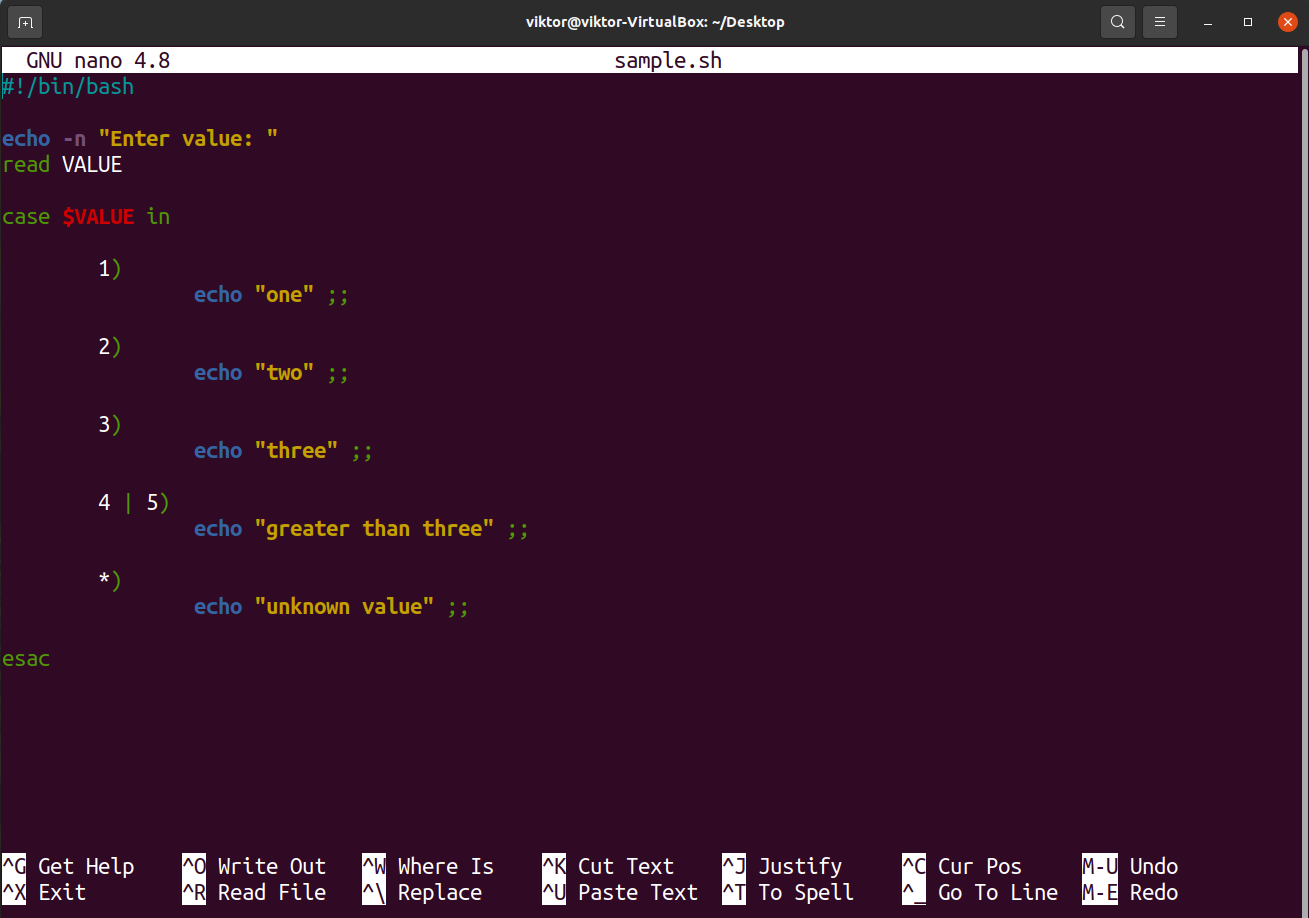
Matching Pattern in Bash Case Statement
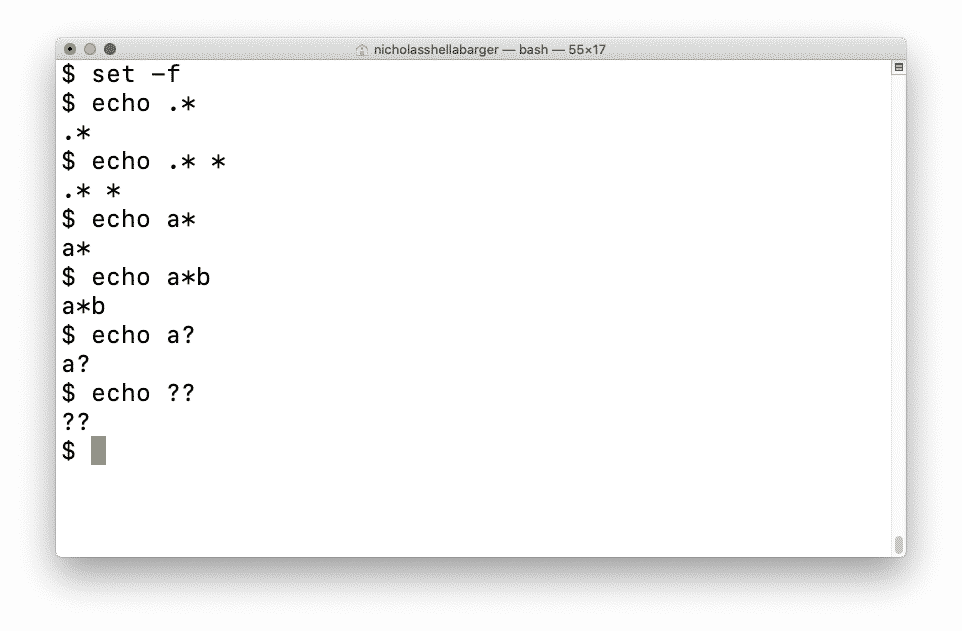
Web If You Wanted To Match Letters, Digits Or Spaces You Could Use:
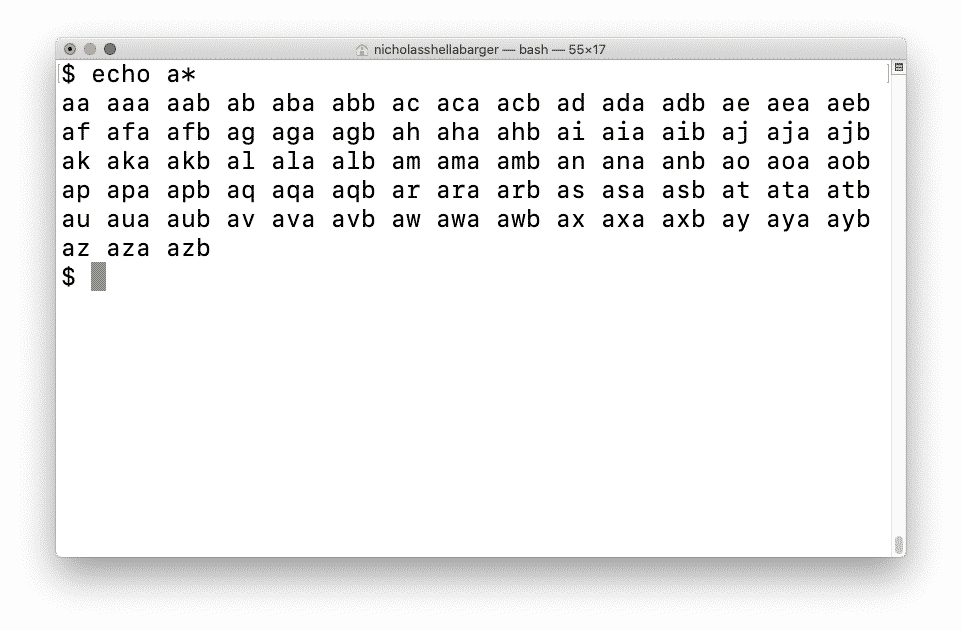
Web The * Is A Special Character In Bash That Represents 0 Or More Characters.
Web Regular Expressions Are A Useful Tool For Pattern Matching In Bash Scripting.
So, This Command Essentially Says, Cat Any Files That Contain 0 Or More Characters, Followed By.txt.
Related Post: